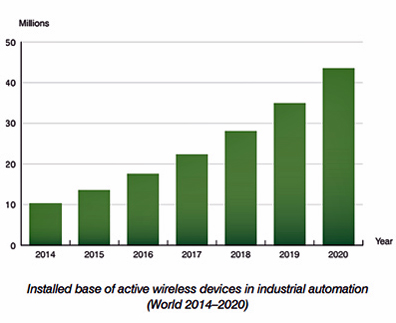
After consulting its Tarot cards and reading the entrails of a white bull, Berg claimed that the number of wireless IoT devices in automation networks will grow to reach 43.5 million by 2020.
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are the most widespread technologies in factory automation while cellular connectivity typically is used for remote monitoring and backhaul communication between plants, the report said.
The increasing popularity of Ethernet based networks in factory automation is one of the key drivers for the popularity of Wi-Fi in such applications.
Tablets and smartphones in mobile HMI solutions is also an important driver for the adoption of Wi-Fi as well as Bluetooth in automation equipment.
Market leaders of 802.15.4 devices include Emerson, Honeywell, GE and Yokogawa are leading vendors in industrial automation. While Siemens, Cisco, Belden, Moxa, Schneider Electric and Eaton are major vendors of Wi-Fi devices. Eaton, GE and Sierra Wireless are important vendors of cellular devices for industrial automation applications, the report said.
Johan Svanberg, Senior Analyst, Berg said that companies were deepening the integration between industrial automation systems and enterprise applications and the promise of IoT is getting more tangible daily.
"Large multinational corporations are beginning to systematically develop and adopt best practices to maximise the benefits of IoT technology in every part of their organisations. IT/OT convergence, smart factories, Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things are all concepts which are part of the ongoing evolution of industrial automation. Innovation in sensor technology, wireless connectivity, energy harvesting, 3D printing, big data and cloud solutions along with seamless exchange of information between devices, systems and people paves the way for improved performance, flexibility and responsiveness throughout the enterprise value chain," Svanberg said.




