Index
- Nvidia Geforce RTX-series is born
- Turing architecture and RTX series
- The new Turing architecture in more details
- Shader improvements and GDDR6 memory
- Nvidia RTX Ray Tracing and DLSS
- The Geforce GTX 2080 Ti and GTX 2080 graphics cards
- Test Setup
- First performance details, UL 3DMark
- Shadow of the Tomb Raider, Assassin’s Creed: Origins
- The Witcher 3, Battlefield 1
- F1 2018, Wolfenstein II: The New Colossus
- Power consumption, temperatures and overclocking
- Conclusion
- All Pages
Nvidia RTX Ray Tracing and DLSS
What make the Nvidia Geforce RTX-series so interesting are not only the advancements in sheer GPU performance but also plenty of new features like Ray Tracing and Deep Learning Super-Sampling (DLSS), which will both push the game development in a different direction, bringing a much realistic graphics to games but also offer a significant performance uplift at no cost, all thanks to RT and Tensor Cores.
Ray Tracing has been the holy grail of graphics for quite some time and while Nvidia implementation with the RTX series might not bring “the real-time Ray Tracing”, it is pushing game developers in the right direction and, thanks to RT Cores, accelerates some ray tracing operations, especially the Bounding Volume Hierarchy Traversal (BVH) and triangle intersection.
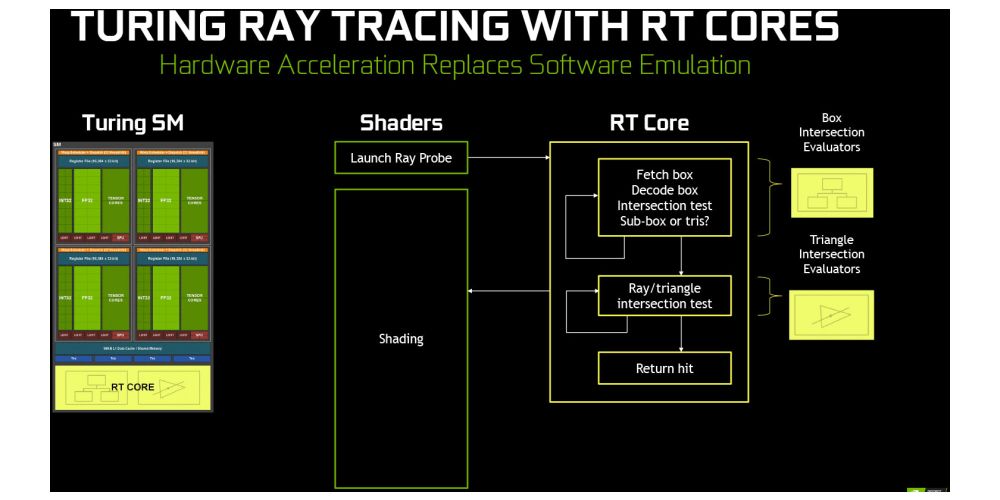
The games will still use rasterization and we won’t see a fully ray traced game for quite some time. On the other hand, RTX Ray Tracing will bring something that Nvidia calls “hybrid rendering”, where ray tracing will be used for specific effects, like global illumination, ambient occlusion, real shadows, reflections, and refractions, without the performance hit that would be seen with rasterization.
Some developers were quite excited and probably the best use scenario will be seen in 4A Games’ Metro Exodus, and they made a neat video showing what can be done with Nvidia RTX Ray Tracing. EA/DICE will also implement some elements of RTX Ray Tracing in Battlefield V, and you can check out the video showing some of those effects as well. Shadow of the Tomb Raider game also used some of these RTX Ray Tracing effects to render realistic shadows so that video can be seen below as well.
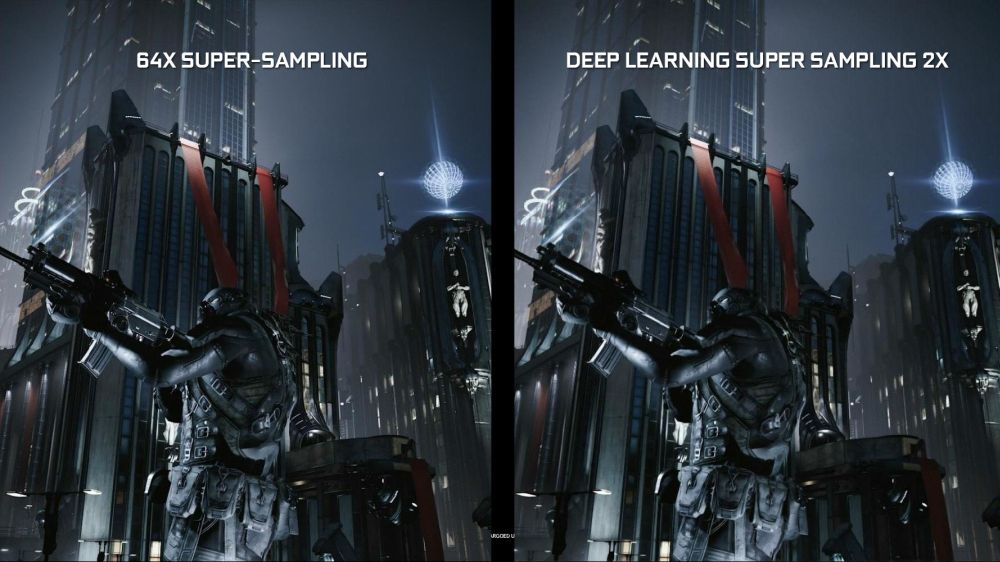
Deep Learning Super-Sampling (DLSS) is an RTX-exclusive anti-aliasing technique which uses a Nvidia-generated “ground truth” image and compiling a DLSS model, which is then pulled from the driver and processed by Tensor cores to provide better image quality than some anti-aliasing techniques (like TAA) without the actual performance impact.

According to Nvidia, in terms of image quality and performance, should bring the quality of the Temporal Anti-Aliasing (TAA) at a much lower performance impact with DLSS as well as higher quality with DLSS 2X, which uses 64x super-sampled images.
You can argue that DLSS pretty much up-scales the image but it is more of a combination of up-scaling, super-sampling, and some other techniques that should bring much better quality without performance impact.
Demos that we saw do look quite impressive but even Nvidia was still vague about what happens at different resolutions so we will have to wait and see how well it will work in games, which essentially, needs to go through Nvidia in order to get DLSS support.





