A paper was submitted at IEEE and it was the first time AMD mentioned sixteen Zen cores wrapped around the GPU and powered by HBM 2 memory. We believe that this is a 16-core processor with 32 thread support and not 32 core as many reported. We will know soon enough and then can have another "we told you so" headline.
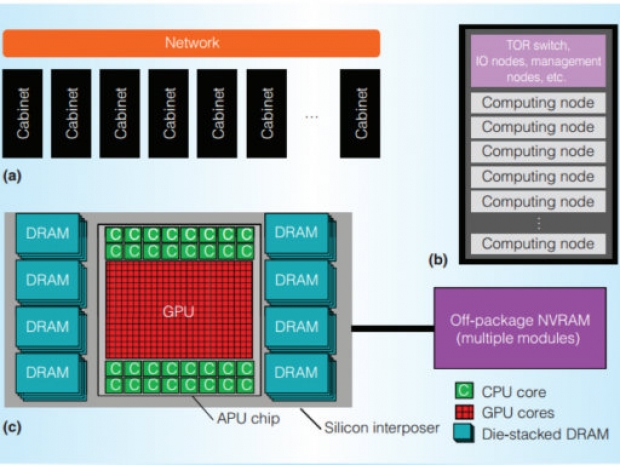
We would not be surprised if we hear more about this AMD processor at the Hot Chips conference on August 23rd. The EHP computing solution uses a silicon interposer and an APU chip that, almost as a raison d'être for AMD over the past several years, packs a GPU and CPU into a well-tuned band. All this will be surrounded by die-stacked DRAM.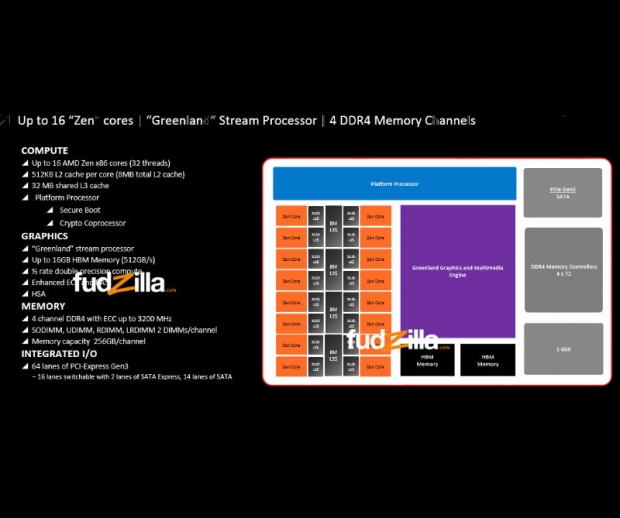
The Italian website that brought this news back to life claims that AMD expects to ship the product between 2016 and 2017. That is the sort of timing you can expect with the rest of the ZEN based cores on the market. One can only hope that it will happen sooner rather than later. AMD needs to get more of the high performance compute market and earn some profits.
The IEEE article gives a bit of light on AMD exascale computer strategy:
Exascale computing requires very high levels of performance capabilities while staying within very stringent power budgets. Hardware optimized for specific functions is much more energy efficient than implementing those functions with general purpose cores. However, there is a strong desire for supercomputer customers to not have to pay for custom components designed only for high-end HPC systems, and therefore high-volume GPU technology becomes a natural choice for energy-efficient data-parallel computing. To fully realize the capabilities of the GPU, we envision exascale compute nodes comprised of integrated CPUs and GPUs (i.e., accelerated processing units or APUs) along with the hardware and software support to enable scientists to effectively run their scientific experiments on an exascale system. [In the paper submitted to IEEE...] We discuss the hardware and software challenges in building a heterogeneous exascale system, and we describe on-going research efforts at AMD to realize our exascale vision.